Are you suffering with Ankle Pain?
So, you are suffering with pain in the ankle? Or maybe your ankles feel weak and it’s hard to balance because your ankles are unstable? Or maybe you have had an ankle injury, been told you have healed but the ankle is not functioning like it used to? Finding the cause of this dysfunction is the key to putting a spring back in your step.
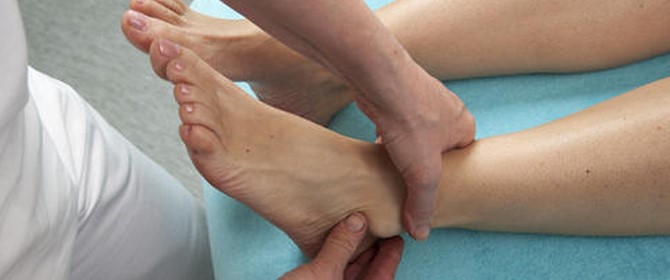
What causes ankle pain?
Sore ankles, weak ankles, ankles that roll in when you stand or move, or ongoing issues from sprained ankles are all problems we treat at the Foot & Leg Centre every day. In fact, many clients that seek our services have experienced an ankle sprain (mild or major) as part of the medical history.
When you suffer an ankle sprain or roll over on your ankle (even years ago), the ankle joint can become displaced from its correct position. Even though the damaged tissue may have healed the resulting displacement can make the ligaments and the bones near the ankle become weak, unstable and not work efficiently. In other words, your body has to work harder to walk and move around, because the structures around the ankle are not in the right place and therefore not working very effectively.
Due to this weakening, it is more likely that ongoing or recurrent sprains or ankle instability can take place in the future. This can cause further injury and trauma to the joint and surrounding tissues. The likelihood of osteo-arthrits developing in the joint is also increased when the structures are not working in the correct position.
How do we fix ankle pain?
The key to fixing ankle pain is to identify and treat the cause. In order to stabilise the joints, and to prevent injury in the future a combination of hands-on foot mobilisation techniques (FMT) and corrective exercises is often recommended.
Through FMT, we can correct the positioning of the bones in the ankle, and the corrective exercises strengthen the specific muscles which help to hold the structure in place.
This treatment corrects the cause of the problem (joint displacement) and gives long term results.
If you have arthritis in your ankle joint, foot mobilisation treatment may benefit you. FMT increases the production of synovial fluid, the oil for the joint. By increasing the production of synovial fluid, the joint can work more efficiently, with less pain. Your practitioner needs to assess the level of arthritis in the joint, and determine whether FMT may benefit your individual case.
Ankle Sprain Management
Let’s face it if you live an active life, participate in sport or just walk around on even ground you can sprain your ankle. The most common type of sprain is a Lateral Ankle Sprain/inversion sprain (or lateral ligament sprain) where the foot rolls outwards, damaging the ligaments on the outside of the ankle. You can also sprain the inside of your ankle (medial ankle sprain). This far less common and typically takes more force for this to occur and damage the ligaments.
In addition to ligament damage there may also be damage to tendons, bone and other joint tissues. Often radiology such as an X-ray should be used to ensure a fracture or bone fragment (avulsion fracture) hasn’t occurred.
Immediate First Aid for an acute ankle injury:
If you have an acute ankle injury (like a sprain) which has resulted in tenderness and swelling in the ankle area, you can apply the RICER treatment principle (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation, and Referral) as soon as possible.
R = Rest. Try to rest the area immediately to reduce pain and prevent further damage.
It is often recommended to start walking (as normally as possible) once partial weight-bearing is tolerable as this is thought to accelerate return to normal activity. Your level of pain and discomfort should be a guide and always trust the advice of your healthcare professional.
I = ICE Applying ice (or cold therapy) can ease the pain, reduce swelling, reduce bleeding (initially) and encourage blood flow (when used later) to assist in healing.
Apply an ice pack or similar immediately following injury for 10 – 15 minutes. This can be repeated every 2 hours.
C = Compression: Using a compression bandage can help reduce bleeding and swelling.
E = Elevation – Putting your foot up uses gravity to help reduce bleeding and swelling by allowing fluids to flow away from the site of injury.
R = Referral – Seek professional advice to accurately diagnose and treat ankle conditions.
Remember there are many different causes and grades to ankle sprains and proper diagnosis can help you achieve a speedy recovery. After the initial first aid management, longer term strengthening and functional rehabilitation is often needed to maximise your recovery outcomes.